Competition policy helps to promote and protect the competitive process and provides a level playing field for all enterprises. Fair and effective competition contributes to improvements in economic efficiency, economic growth and development, as well as consumer welfare.
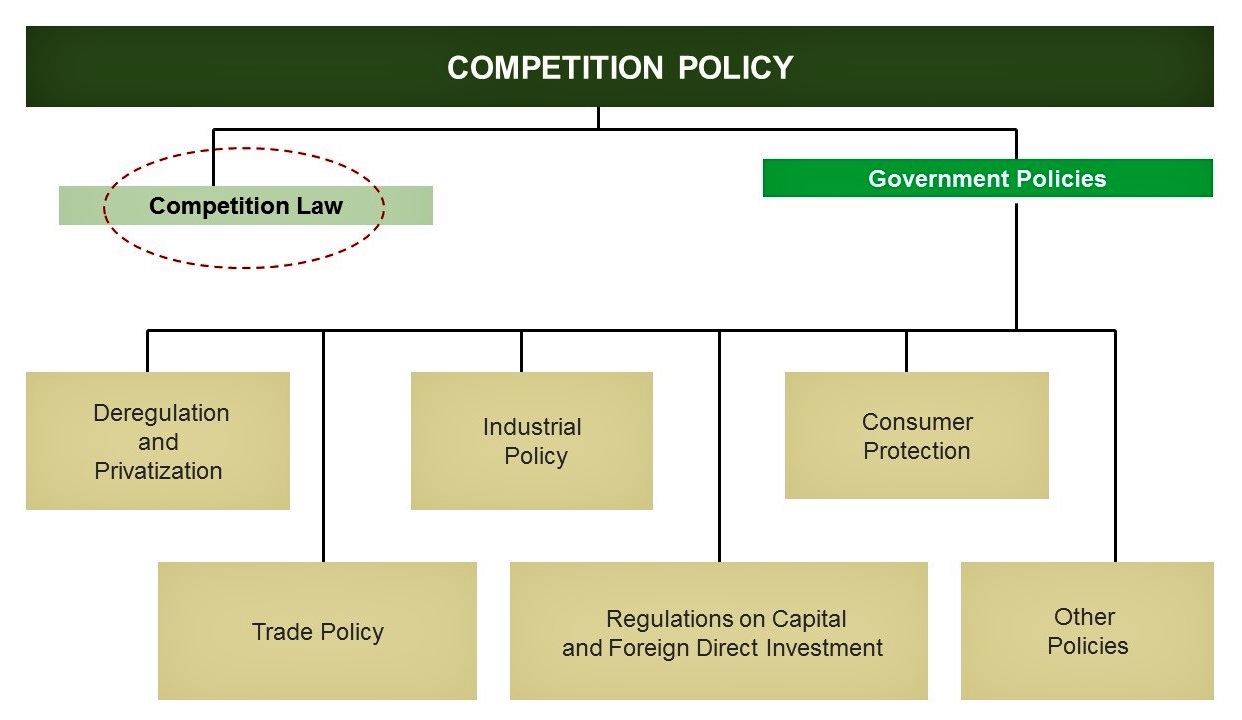
Broadly speaking, competition policy can be defined as a government policy that helps maintain the level of competition in markets. This includes governmental measures that directly affect the behaviour of enterprises, as well as the structure of industries and markets.
Competition policy basically covers:
- A set of policies that promote competition in local and national markets, for example policies to eliminate restrictive trade practices, favour market entry and exit, reduce unnecessary governmental interventions and put greater reliance on market forces; and
- A competition law that comprises specific legislation and regulations aimed at preventing anti-competitive agreements, abuse of dominance and anti-competitive mergers.
Competition policy complements other government policies such as trade policy, industrial policy and regulatory reform, and accommodates other economic and social objectives to enhance technological advancement, industrial diversification and job creation.